Ginger (Zingiber officinale) is widely celebrated as a natural remedy for nausea, inflammation, and digestive issues.
Its rich composition of antioxidants, anti-inflammatory compounds, and essential nutrients makes it a staple in many households.
However, while ginger offers numerous health benefits, it’s not suitable for everyone.
#1. If You Have a Bleeding Disorder
Ginger is known to have natural blood-thinning properties, thanks to its active compounds like gingerol. While this can benefit circulation and heart health, it poses a risk for individuals with bleeding disorders.
If you’re already taking blood-thinning medications like warfarin, aspirin, or heparin, consuming ginger can amplify these effects, leading to complications.

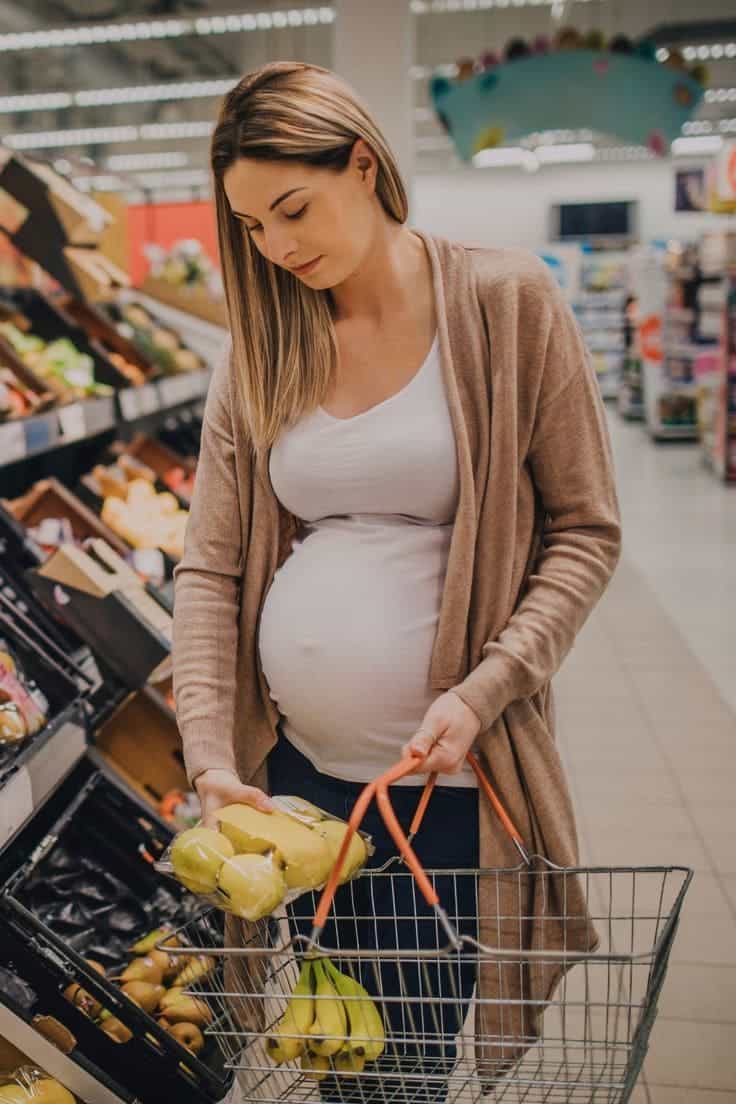
#2. If You’re Pregnant
While ginger is often used to alleviate morning sickness during early pregnancy, excessive consumption can lead to unwanted side effects.
Experts generally recommend limiting ginger intake during pregnancy to less than 1 gram per day.

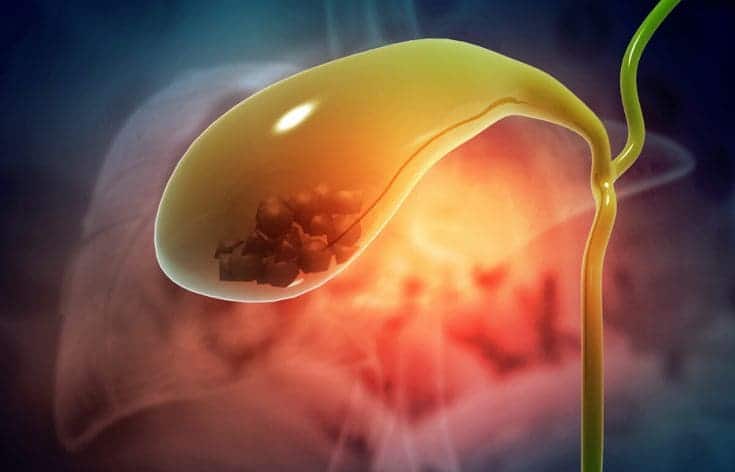
#3. If You Have Gallstones
Ginger stimulates bile production, which can be problematic for individuals with gallstones. Excess bile secretion may worsen symptoms by causing more pain or triggering an attack.
If you have gallbladder issues or suspect gallstones, it’s best to avoid ginger and consult a healthcare professional for safer dietary choices.
#4. If You’re Taking Certain Medications
Ginger can interact with various medications, leading to unintended side effects. Avoid ginger if you’re taking:
- Anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs: Ginger’s blood-thinning properties may increase the risk of bleeding.
- Diabetes medications: Ginger lowers blood sugar levels, which can lead to hypoglycemia if combined with diabetes medications like insulin.
- Blood pressure medications: Ginger may lower blood pressure excessively when taken alongside antihypertensive drugs, causing dizziness or fainting.
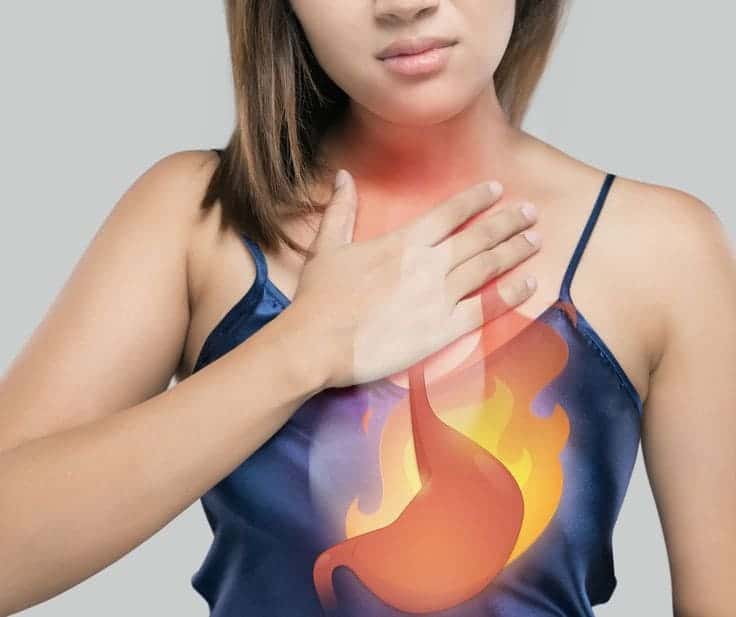
#5. If You Have Acid Reflux or GERD
Ginger is a well-known remedy for nausea and indigestion, but in some cases, its spicy nature can irritate the esophagus and worsen symptoms of acid reflux or GERD.
If you notice increased heartburn or discomfort after consuming ginger, it’s best to limit or avoid it altogether.
#6. If You Have Low Blood Pressure
Ginger is a natural vasodilator, meaning it helps widen blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
While this can benefit individuals with hypertension, those with already low blood pressure may experience dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting after consuming ginger.
#7. If You’re Underweight
Ginger is known to enhance metabolism and suppress appetite, which can lead to weight loss.
If you’re underweight or struggling to maintain a healthy weight, consuming ginger regularly might not be ideal. It could further suppress your appetite and interfere with your efforts to gain weight.
#8. If You Have a History of Allergies
Although rare, some individuals may experience an allergic reaction to ginger. Symptoms include itching, swelling, hives, or difficulty breathing.
If you notice any allergic symptoms after consuming ginger, discontinue use immediately and seek medical attention.
How Much Ginger Is Safe to Consume?
For most individuals, consuming up to 4 grams of ginger daily is considered safe. However, if you fall into any of the categories above, it’s essential to limit or avoid ginger altogether.
Always start with small amounts and monitor your body’s reaction, especially if you’re introducing ginger into your diet for the first time.

Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice.
Always consult with your healthcare provider before making dietary changes or using natural remedies, especially if you have underlying conditions or take medications.







